Connecting Multiple Databases With Spring Data JPA – Source Code On GitHub
Usually, when you build an application you intend to connect to a single database. Its often not required to connect to multiple data sources unless you working on an ETL kind of project.
Connecting Multiple Databases With Spring Data JPA:
In this article, we will see how you can Configure multiple Databases and Connect to Multiple databases with Spring Data JPA
Softwares used
- Spring Boot 2.0.2.RELEASE
- Spring Data JPA
- Java 8
- Oracle XE
- MySQL
- Maven
- Eclipse
To simulate the real-life scenario, in our demonstration we will connect to two databases Oracle and MySQL.
Maven Dependencies
Below are some of the key maven dependencies that we have used.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/oracle/ojdbc6 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.oracle</groupId> <artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId> <version>11.2.0</version> </dependency> <!-- Database and Pooling --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> |
Now, we need to make a note here. Oracle jars are not available through maven. So you need to download the jar and install in your local repository before you build your project.
You can read this article – How to add Oracle JDBC driver in your Maven local repository
We will define database details in our properties file. The file will look like below
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
#Oracle DB Config db.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect db.driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver db.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe db.user=pavans db.password=****** #MySQL DB Config mysql.db.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect mysql.db.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mysql.db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/localdb?useSSL=false mysql.db.user=lessroot mysql.db.password=****** |
Now when we define two data source beans, Spring needs to know which one is primary and which bean is treated as secondary. If you don’t define them Spring will fail to start your application as there will be two beans of the same type it tries to make ready for injection.
You can define any bean primary with annotation @Primary
We will configure our data source bean in the similar way we have done in one of the previous articles.
Read – Java Web Application Starter Template with Spring Boot
Primary Datasource Configuration
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 |
@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @EnableJpaRepositories( entityManagerFactoryRef = "entityManagerFactory", transactionManagerRef = "transactionManager", basePackages = "com.opencodez.dao.oracle.repo" ) public class PrimaryDbConfig { public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE = "hibernate.jdbc.batch_size"; public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL = "hibernate.show_sql"; public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL = "hibernate.format_sql"; public static final String[] ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN = { "com.opencodez.dao.oracle.domain" }; public static final String DB_URL = "db.url"; public static final String DB_USER = "db.user"; public static final String DB_PASSWORD = "db.password"; public static final String DB_DRIVER = "db.driver"; public static final String DB_DIALECT = "db.dialect"; @Autowired private Environment env; @Bean public AnnotationMBeanExporter annotationMBeanExporter() { AnnotationMBeanExporter annotationMBeanExporter = new AnnotationMBeanExporter(); annotationMBeanExporter.addExcludedBean("dataSource"); annotationMBeanExporter.setRegistrationPolicy(RegistrationPolicy.IGNORE_EXISTING); return annotationMBeanExporter; } @Bean(destroyMethod = "close") @Primary public DataSource dataSource() { ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); try { dataSource.setDriverClass(env.getProperty(DB_DRIVER)); } catch (PropertyVetoException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } dataSource.setJdbcUrl(env.getProperty(DB_URL)); dataSource.setUser(env.getProperty(DB_USER)); dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty(DB_PASSWORD)); dataSource.setAcquireIncrement(5); dataSource.setMaxStatementsPerConnection(20); dataSource.setMaxStatements(100); dataSource.setMaxPoolSize(500); dataSource.setMinPoolSize(5); return dataSource; } @Bean(name = "transactionManager") @Primary public JpaTransactionManager jpaTransactionManager() { JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager(); transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactoryBean().getObject()); return transactionManager; } @Bean(name = "entityManagerFactory") @Primary public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean() { LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdaptor()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceProviderClass(HibernatePersistenceProvider.class); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceUnitManager(persistenceUnitManager()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceUnitName("orcl"); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan(ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaProperties(jpaHibernateProperties()); return entityManagerFactoryBean; } @Bean @Primary public DefaultPersistenceUnitManager persistenceUnitManager() { DefaultPersistenceUnitManager persistenceUnitManager = new DefaultPersistenceUnitManager(); persistenceUnitManager.setDefaultDataSource(dataSource()); return persistenceUnitManager; } private HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdaptor() { HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter(); vendorAdapter.setDatabasePlatform(env.getProperty(DB_DIALECT)); vendorAdapter.setShowSql(false); return vendorAdapter; } private Properties jpaHibernateProperties() { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL)); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE)); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL)); return properties; } } |
Please take a look at how we have added @Primary annotation on the data source, entity manager factory. Also, we have given references to these beans with the qualifier in the @EnableJpaRepositories annotation.
Secondary Datasource Configuration
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 |
@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @EnableJpaRepositories( entityManagerFactoryRef = "mysqlEntityManager", transactionManagerRef = "mysqlTransactionManager", basePackages = "com.opencodez.dao.mysql.repo" ) public class SecondaryDbConfig { public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE = "hibernate.jdbc.batch_size"; public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL = "hibernate.show_sql"; public static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL = "hibernate.format_sql"; public static final String[] ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN = { "com.opencodez.dao.mysql.domain" }; public static final String DB_URL = "mysql.db.url"; public static final String DB_USER = "mysql.db.user"; public static final String DB_PASSWORD = "mysql.db.password"; public static final String DB_DRIVER = "mysql.db.driver"; public static final String DB_DIALECT = "mysql.db.dialect"; @Autowired private Environment env; @Bean public AnnotationMBeanExporter annotationMBeanExporter() { AnnotationMBeanExporter annotationMBeanExporter = new AnnotationMBeanExporter(); annotationMBeanExporter.addExcludedBean("dataSource"); annotationMBeanExporter.setRegistrationPolicy(RegistrationPolicy.IGNORE_EXISTING); return annotationMBeanExporter; } @Bean(name = "mysqlDataSource", destroyMethod = "close") public DataSource dataSource() { ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); try { dataSource.setDriverClass(env.getProperty(DB_DRIVER)); } catch (PropertyVetoException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } dataSource.setJdbcUrl(env.getProperty(DB_URL)); dataSource.setUser(env.getProperty(DB_USER)); dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty(DB_PASSWORD)); dataSource.setAcquireIncrement(5); dataSource.setMaxStatementsPerConnection(20); dataSource.setMaxStatements(100); dataSource.setMaxPoolSize(500); dataSource.setMinPoolSize(5); return dataSource; } @Bean(name = "mysqlTransactionManager") public JpaTransactionManager jpaTransactionManager() { JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager(); transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactoryBean().getObject()); return transactionManager; } @Bean(name = "mysqlEntityManager") public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean() { LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdaptor()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceProviderClass(HibernatePersistenceProvider.class); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceUnitManager(persistenceUnitManager()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceUnitName("mysql"); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan(ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaProperties(jpaHibernateProperties()); return entityManagerFactoryBean; } @Bean(name = "mysqlpersistenceUnitManager") public DefaultPersistenceUnitManager persistenceUnitManager() { DefaultPersistenceUnitManager persistenceUnitManager = new DefaultPersistenceUnitManager(); persistenceUnitManager.setDefaultDataSource(dataSource()); return persistenceUnitManager; } private HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdaptor() { HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter(); vendorAdapter.setDatabasePlatform(env.getProperty(DB_DIALECT)); vendorAdapter.setShowSql(false); return vendorAdapter; } private Properties jpaHibernateProperties() { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_FMT_SQL)); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_JDBC_BATCH_SIZE)); properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL, env.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL)); return properties; } } |
The secondary dao config doesn’t have @Primary annotation but the bean qualifiers have to be uniquely referenced.
So far we have completed our database configuration now let us use them. I have defined two tables in each of the database TblOracle and TblMysql. Each of these tables has the same structure. Below are their corresponding entities
TblOracle
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
@Entity @Table(name = "TBL_ORCL") public class TblOracle { @Id @GeneratedValue @Column(name = "MESSAGE_ID") private Long id; @Column(name = "MESSAGE") private String message; @Column(name = "CREATED_DATE") private Date created; //Getters and Setters } |
TblMysql
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
@Entity @Table(name = "tbl_mysql") public class TblMysql { @Id @GeneratedValue @Column(name = "MESSAGE_ID") private Long id; @Column(name = "MESSAGE") private String message; @Column(name = "CREATED_DATE") private Date created; //Getters and Setters } |
Corresponding persistence.xml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd" version="1.0"> <persistence-unit name="orcl" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <class>com.opencodez.dao.oracle.domain.TblOracle</class> <exclude-unlisted-classes>true</exclude-unlisted-classes> </persistence-unit> <persistence-unit name="mysql" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <class>com.opencodez.dao.mysql.domain.TblMysql</class> <exclude-unlisted-classes>true</exclude-unlisted-classes> </persistence-unit> </persistence> |
For our demo, we will define a simple rest controller and will use the Spring Data JPA Repositories in them.
We will define repositories as
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
@Autowired private OracleMessageRepo oracleMessageRepo; @Autowired private MysqlMessageRepo mysqlMessageRepo; |
These will be referenced in an example as
|
1 2 3 |
List<TblOracle> messages = oracleMessageRepo.findAll(); List<TblMysql> messages = mysqlMessageRepo.findAll(); |
Above is the usage we have seen using JPA repositories. What if we want to use the traditional way by defining entity manager?
Define Entity Manager
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
@Autowired @Qualifier("entityManagerFactory") private EntityManager oracleEM; @Autowired @Qualifier("mysqlEntityManager") private EntityManager mysqlEM; |
See how we have autowired the factories, we need to provide the unique qualifier we have set in the config.
Usage
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
try { String sql = "select t from TblOracle t"; Query query = oracleEM.createQuery(sql); List<TblOracle> list =(List<TblOracle>)query.getResultList( ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { String sql = "select t from TblMysql t"; Query query = mysqlEM.createQuery(sql); List<TblMysql> list=(List<TblMysql>)query.getResultList( ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
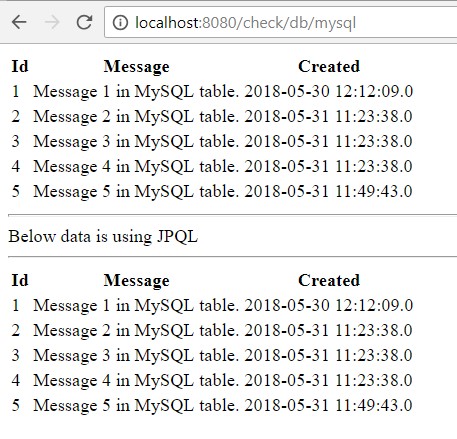
Check below screen to see them in action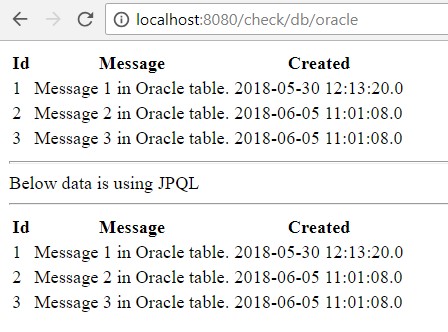
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen how it is easy to connect to Multiple databases with Spring Data JPA. We have seen what precautions we need to take while doing the configuration for multiple databases.
The complete code is available at our GitHub repo. Please feel free to download and try.
Download Code